How to run multiple simulations in a batch
When searching for the right physical and geometrical parameters, more than one simulation is needed to evaluate and compare the results and impact of different parameter values.
To save time, you can prepare multiple simulation cases and run them successively over night or weekend, without the need to manually run each simulation.
When to use batch running?
Running multiple cases in sequence or successive running is useful when the impact on the results of some physical or geometrical parameters must be determined.
For example, when searching for the best patch inset geometry, different geometrical designs must be tested. To do that, multiple cases with different geometry settings must be run to compare the results.
To ease the running of many different cases, prepare and run all of them during night or weekend, and evaluate the different results in the next morning!
How to set up batch running?
To run different CENOS cases successively, you need to create a .bat file, in which you define which cases and in what order you want to calculate. Then simply double-click on the .bat file to start the calculations.
In this example we will set up a successive running of 3 cases.
1. Open Notepad
Notepad is a built-in Windows code editor. Open it by typing Notepad in the Windows Search line and clicking Enter.
2. Define the sequence
To define the cases you want to run, you need to write a command line for each case which defines with what to run it and where to find the case file. The basic structure of this command consists of 2 parts - "CENOS path", where CENOS is installed and from where it is started, and "case path" to the case folder you want to run.
To find CENOS path, right-click on CENOS shortcut and select Properties. The CENOS path will be already highlighted as Target - simply copy and paste it into the Notepad.
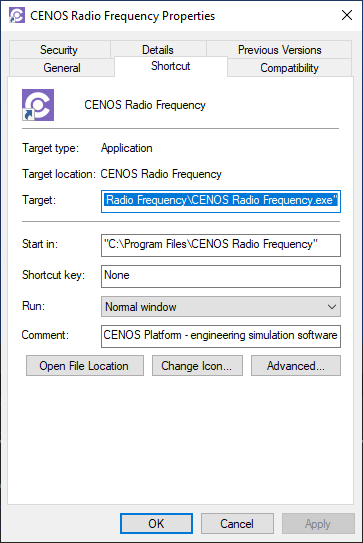
To find case path, in File Explorer go to the case folder and copy its address from the Address Bar.
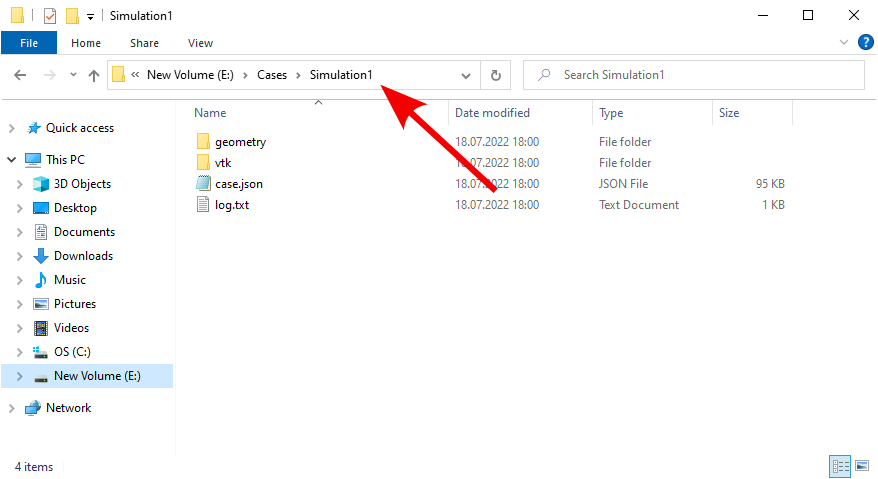
In this example we will set up successive running for 3 cases. Simply write the command for each case in its own line.
note
To make sure the console window does not close after the end of calculations, write pause after case command lines.
important
Put both paths inside quotation marks, otherwise the spacing will break the command!
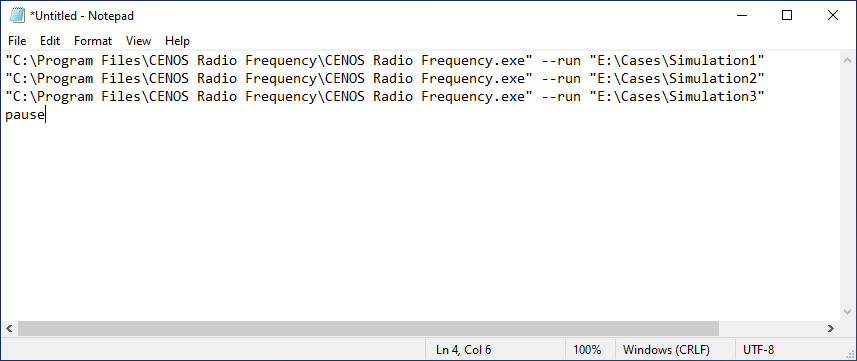
3. Save as .bat file
In Notepad click File -> Save As. Change Save as type to All Files (.), and manually save the file as Batch file by naming it, for example, as sequence.bat.
4. Run the simulations
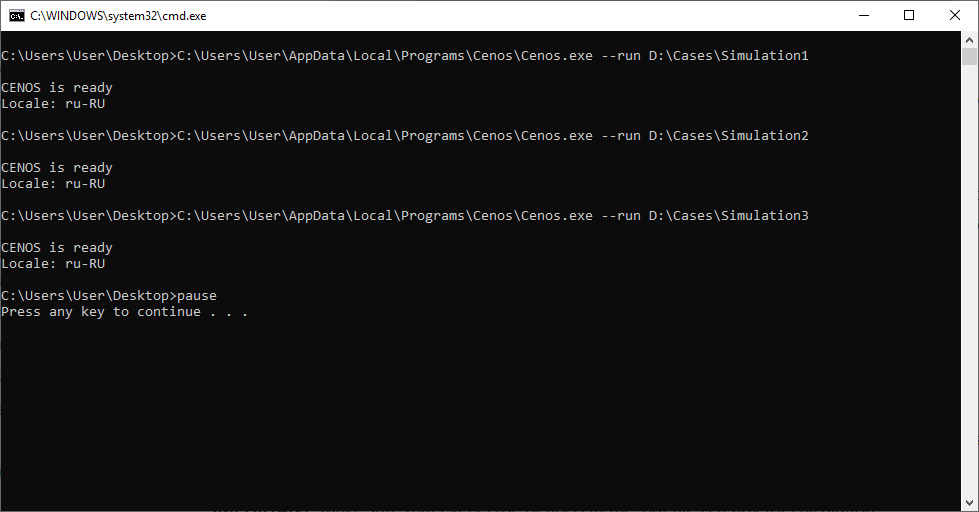
After the Batch file has been created, double-click on it to start the calculation. A console window will open, from which every case defined in the .bat file will be run. A CENOS window will automatically open, the case will calculate, save the results, close CENOS window and go to the next simulation.
When all simulations will be calculated, the console window will stay open, because pause was written in the end of the .bat file commands. This is helpful to know simulations have been calculated successfully.
Limitations
Case setup
If one of the case folders defined in the .bat file will have incomplete physical definition such as missing material, current value etc. meaning that it cannot be run, it will be skipped and not calculated.
note
Make sure that every case defined in the .bat file is ready for calculation!